A surgery that alters the labia minora or majora, the skin folds around the vaginal opening.
This procedure is often pursued for aesthetic reasons, to alleviate discomfort from enlarged labia.

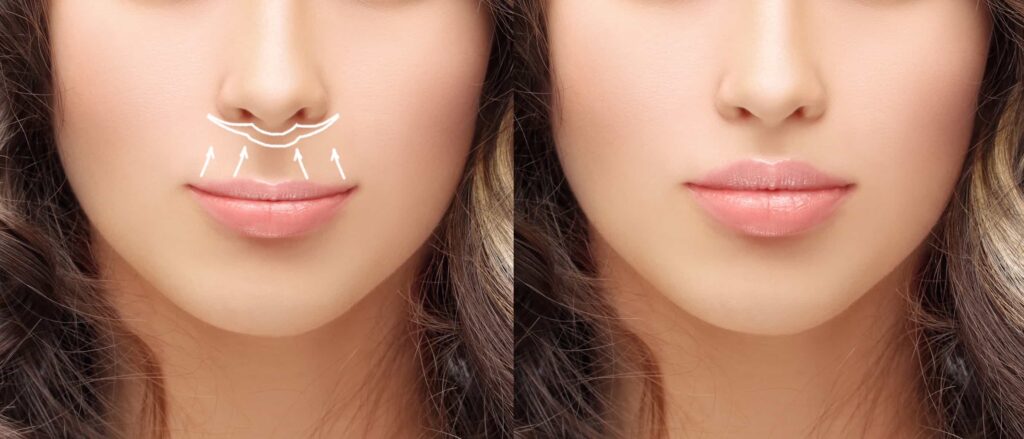
Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure that involves the alteration of the labia minora or labia majora, the folds of skin surrounding the vaginal opening. This procedure is often sought for aesthetic reasons, to reduce discomfort caused by enlarged labia, or to improve hygiene.
It can be performed under local or general anesthesia and typically involves excision of excess tissue to achieve the desired shape and size.
The best candidates for labiaplasty are healthy women who have elongated or thickened labia that interferes with daily hygiene, sexual activities, or self-confidence
– Women may choose labiaplasty for various reasons.
– Improved sexual confidence is commonly reported post-procedure.
– Greater satisfaction with sexual experiences often follows labiaplasty.
– Some women find enhanced comfort in sporting activities after labiaplasty.
– The procedure can facilitate better hygiene in the intimate area.
Risks associated with labiaplasty include:
– Bleeding, hematoma and infection
– Wound opening (dehiscence)
– Prolonged healing
– Discomfort during sexual intercourse
– Need for revisional surgery
– Changes or difficulty in achieving orgasm
– Pain at the incision site
– Changes in skin sensation
First, you and your surgeon will discuss why you want to undergo labiaplasty. You’ll discuss your expectations and goals, as well as the risks of the surgery. They’ll conduct a psychological exam and ask about depression and anxiety.
Before the Surgery:
Either general anesthesia, which puts you completely to sleep, or local anesthesia with sedation, so you feel relaxed but still awake.
During the Procedure:
The surgery itself usually lasts about 1 to 2 hours.
Two main approaches exist for labia reduction:
1. Trim procedure: The surgeon removes excess tissue from the edges of the labia minora to align them with or inside the labia majora.
2. Wedge procedure: A wedge-shaped section is removed from the inner areas of the labia minora, preserving the submucosa for a natural appearance. A similar technique is used for labia majora.
The surgeon will carefully remove any excess tissue using either a scalpel or a laser, then stitch everything back together.
In the first week, it’s normal to experience some discomfort like pain, swelling, bruising, and itching. You might also notice some drainage and, in some cases, a mild fever. Make sure to take any medication your surgeon prescribes to help manage these symptoms.
Dressing Comfortably:
Opt for loose-fitting clothing to help avoid any rubbing on the surgical area, which can help speed up your recovery.
Going to the Bathroom:
You might find urination a bit painful for a few days. To make it easier, try urinating in the shower or running warm water over the area, which can help soothe the discomfort.
Taking it Easy:
It’s really important to give your body time to heal. Try to avoid physical activities for about 4 to 6 weeks, and hold off on any sexual activity for at least 4 weeks.
Watch for Complications:
Following your surgeon’s post-operative instructions is crucial. If you notice any signs of complications, like an infection, bleeding, or if the stitches come apart, don’t hesitate to reach out to your surgeon right away.
The initial swelling, tenderness, and temporary discoloration typically diminish within the first few weeks following the surgical procedure.
Most swelling subsides within six weeks; however, it may require four to six months for the swelling to resolve completely, allowing for the final results of the labiaplasty to be assessed.
Generally, there is minimal to no scarring associated with this procedure.
Surgery carries inherent risks, including complications related to anesthesia and bleeding. While such complications are uncommon, they can arise during the procedure. There is also the possibility of removing either too much or too little tissue, which can lead to further issues. Other risks include the potential for infection, as well as wound breakdown and scarring. Patients may also face ongoing pain, discomfort during sexual activity, or a decrease in sensitivity.
Estimates from organizations, including the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, indicate that the average cost of a labiaplasty ranges from $4,000 to $6,000.

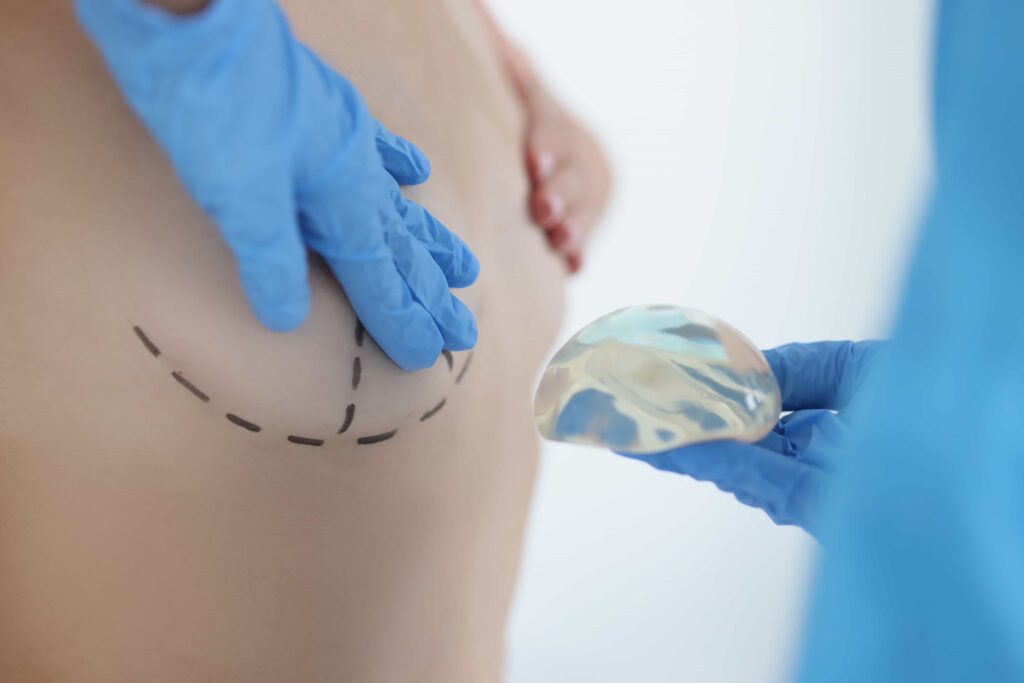
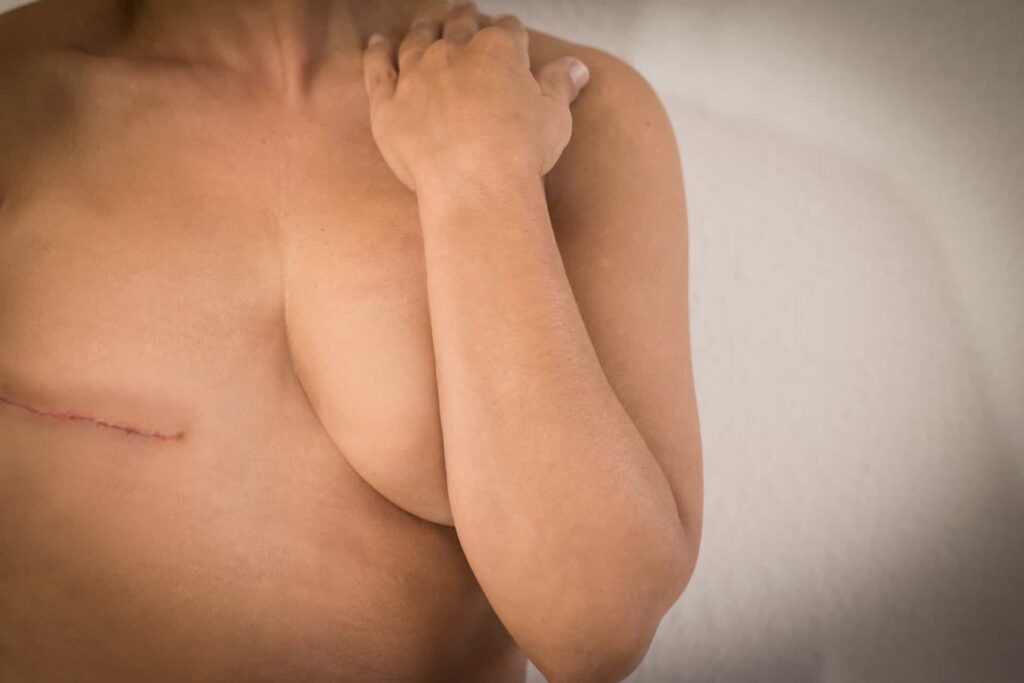



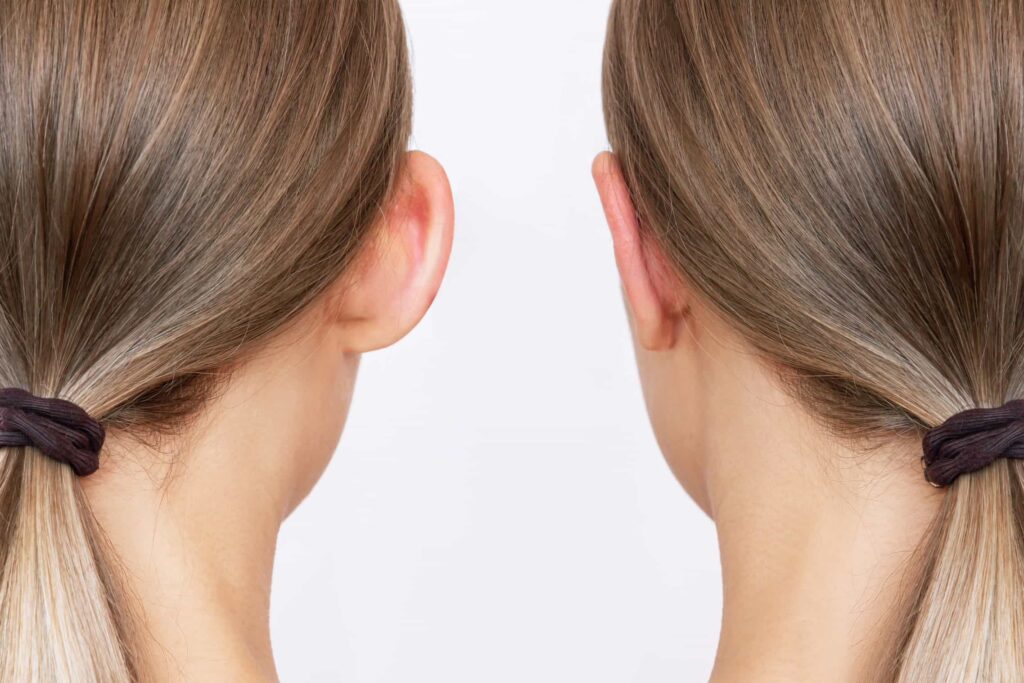
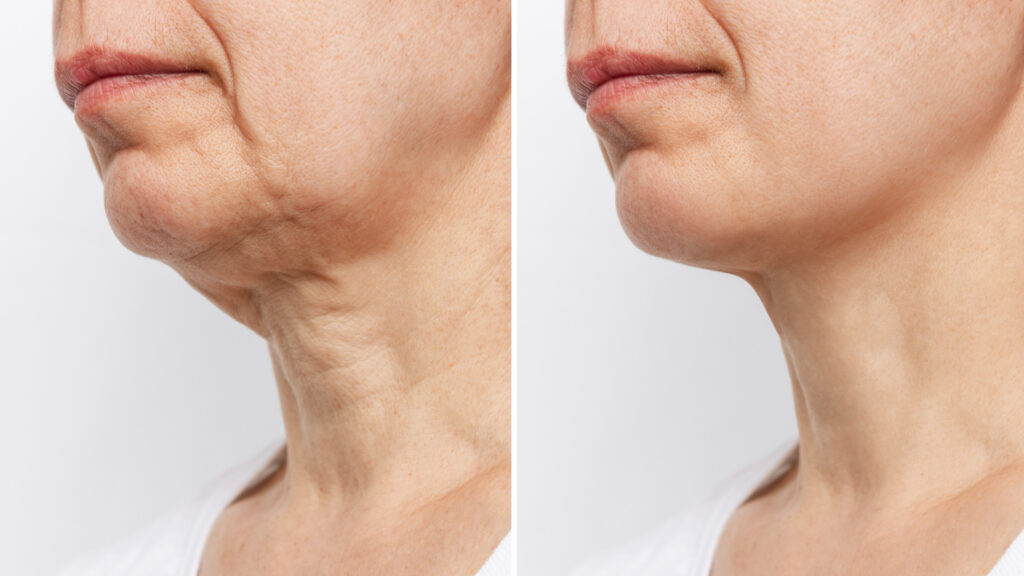


Fat grafting is a procedure that enhances and naturally adds volume to areas of the body by using your own…