Asurgical procedure that involves relocating existing hair follicles to areas that are thinning or lacking hair.
Hair transplantation involves extracting small grafts or larger scalp sections from a donor area and cutting them into smaller pieces for use as grafts.
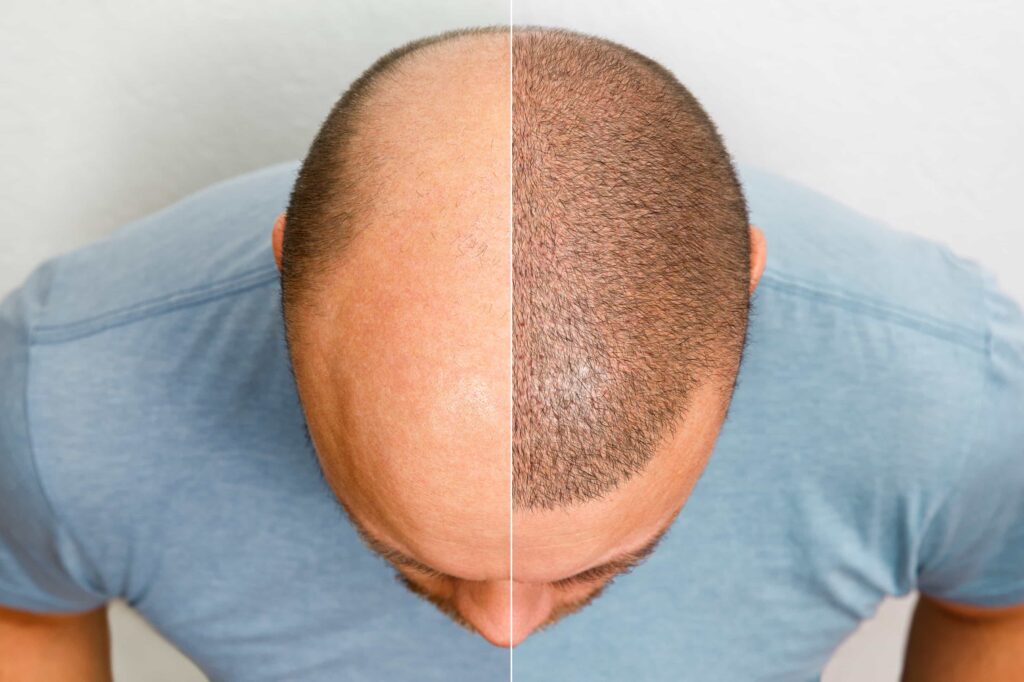

A hair transplant is a surgery that moves hair to bald or thinning areas. First, doctors usually perform this when other treatments don’t work. Next, a dermatologist or plastic surgeon takes hair from a donor site, usually the back of the head. Then, they place it where hair is missing. Finally, the hair grows naturally after healing.
Types of Hair Transplants
•FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): The doctor removes a strip of scalp with hair, then separates it into small grafts. This method works well for advanced hair loss but leaves a thin scar.
•FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): The doctor uses tiny circular incisions to remove individual hair follicles. This method leaves little scarring and offers a faster recovery.
•DHI (Direct Hair Implantation): The doctor removes and places each follicle in one step. It allows for a dense, natural-looking result without needing prior incisions.
•NeoGraft: This is an automated technique that extracts and implants hair with minimal scarring. Doctors can also use hair from other parts of the body.
When choosing a hair transplant, your doctor will first consider your hair loss and goals.
Next, FUE works best for mild to moderate hair loss, while FUT is better for more severe cases.
Also, FUE usually has a faster recovery and may cost differently than FUT.
In addition, winter is a great time for surgery because less sun and sweat help your scalp stay clean and heal well.
Finally, NeoGraft is a modern option. It automates the process, leaves little scarring, heals quickly, and can use hair from different body areas.
-Natural results: Both Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) techniques produce natural-looking hairlines when performed by proficient surgeons.
-Permanent Restoration: Transplanted hair provides a durable solution.
-Minimal Scarring: The FUE technique results in tiny, nearly imperceptible scars, making it an appropriate choice for individuals who prefer shorter hairstyles.
-Outpatient Procedure: These procedures are generally conducted on an outpatient basis, facilitating a prompt return to daily activities.
-Cost Variation: FUE procedures are pricier than FUT due to the complexity of graft extraction.
-Risk of Complications: Postoperative risks, such as infection or bleeding, are rare but possible.
-Scarring: FUT leaves a linear scar that may be visible with short hairstyles.
A hair transplant has two main steps: harvesting and implantation.
Harvesting:
Surgeons use one of two methods to collect hair follicles.
In FUSS, the surgeon removes a strip of hair-bearing skin from the back of the scalp. This area resists hair loss and makes a good donor site. The strip is then cut into individual grafts.
In FUE, the surgeon uses a small tool called a micro punch to remove grafts one by one from the donor area.
Implantation:
After harvesting enough grafts, the surgeon makes small cuts in the thinning or bald areas of the scalp. Then, they place each graft into these incisions to create a natural look.
Recovery after a hair transplant varies based on the procedure. Most patients feel mild discomfort, swelling, and scabbing around both donor and recipient areas.
In the first few days, keep the scalp clean to lower the risk of infection. Use a mild shampoo as your surgeon directs. Avoid touching, scratching, or picking at the treated area to protect the new hair follicles.
Follow your surgeon’s medication instructions. This often includes antibiotics and pain relievers. Also, avoid strenuous activity, direct sunlight, and hair products early in recovery.
Recovery Timeline:
•Day 1: Remove bandages.
•Day 2: Gently wash your hair.
•Days 3–5: Return to work and light activity.
•Day 10: Have stitches removed.
•Week 3: Resume exercise and sports.
Most people see about 60% of new hair growth within 6 to 9 months after a hair transplant. Additionally, some surgeons may suggest using minoxidil (Rogaine) to boost growth, though its results are not guaranteed.
However, full results can take up to a year. During this time, it’s normal for the transplanted hair to shed as part of the healing process. After shedding, the hair usually grows back. In some cases, to achieve a natural look, patients may need more than one procedure.
Like any surgical procedure, transplants carry certain risks. For example, these can include complications such as bleeding and infection. In addition, there is a possibility of scarring. Patients may also experience new hair growth that looks unnatural. Therefore, it’s important to be aware of these potential outcomes when considering a transplant.
The typical price range for a hair transplant is between $6,000 and $12,000. However, some procedures may cost more than $15,000. In addition, several factors influence the total cost. For example, the type of procedure chosen and the number of grafts needed can significantly affect the final price.






Fat grafting is a procedure that enhances and naturally adds volume to areas of the body by using your own…