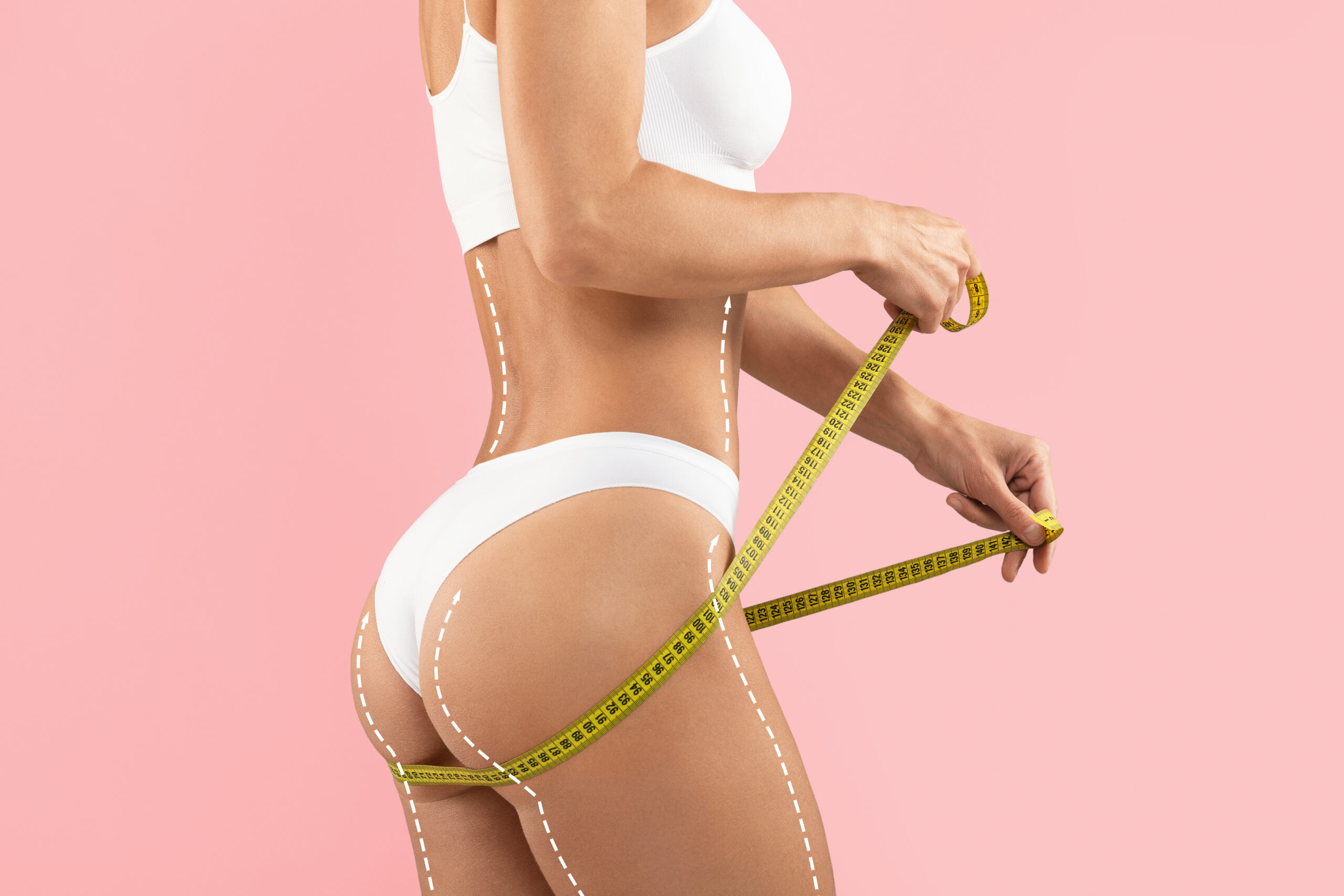
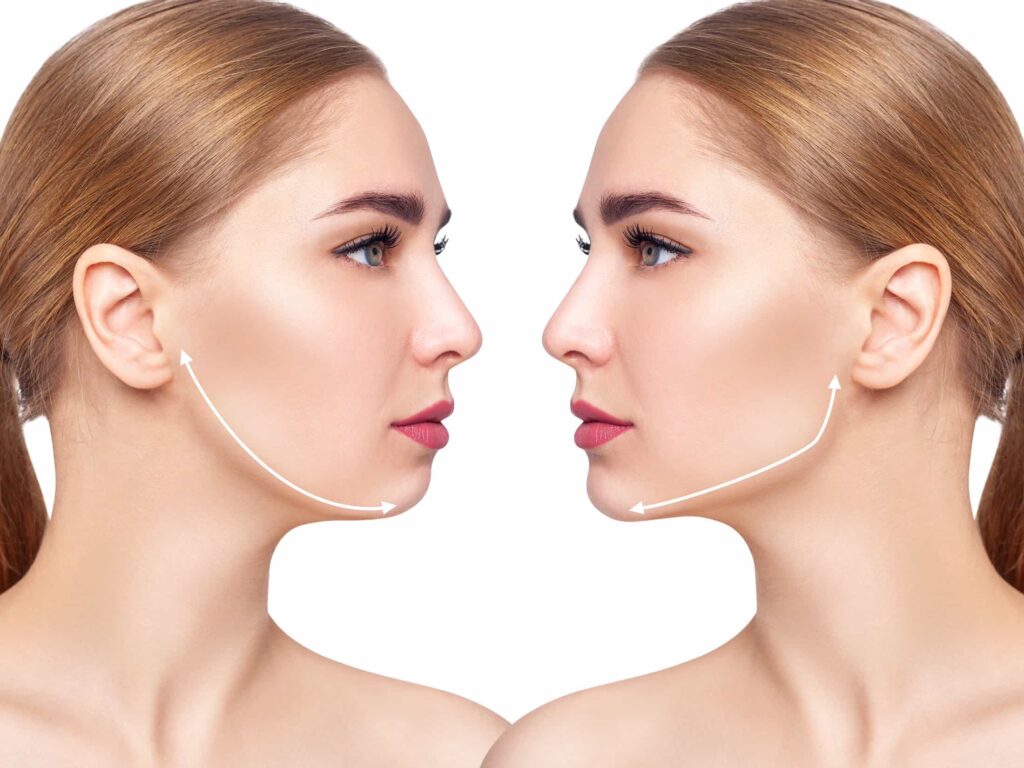
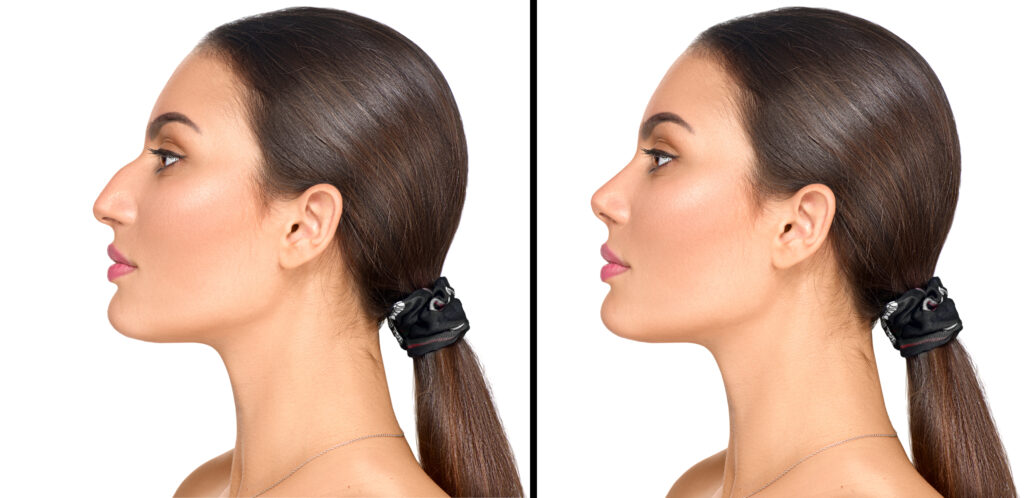
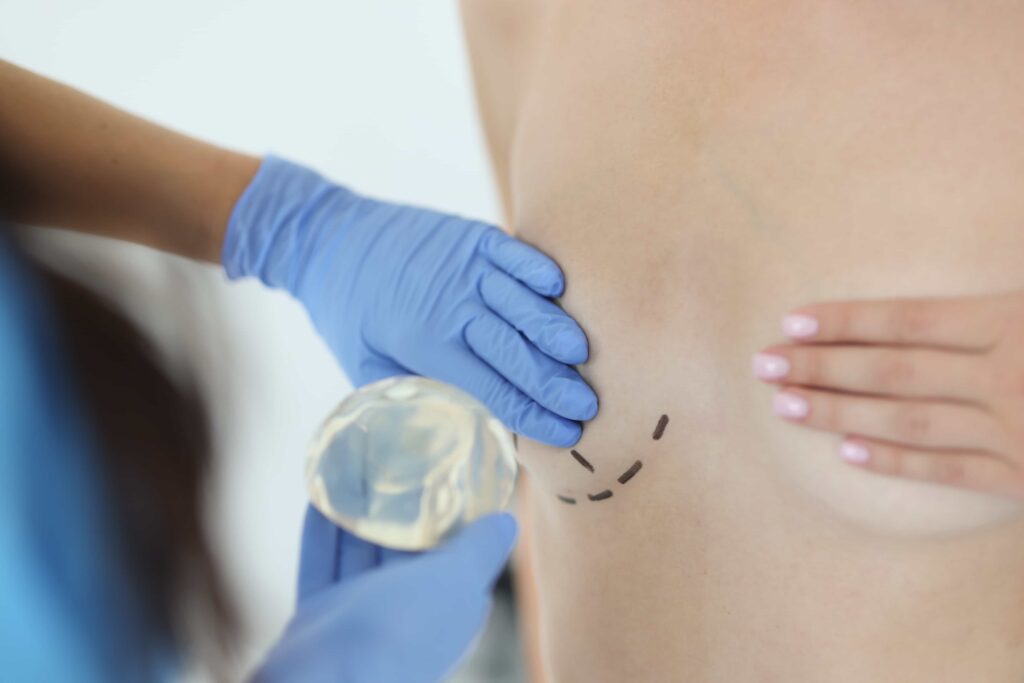
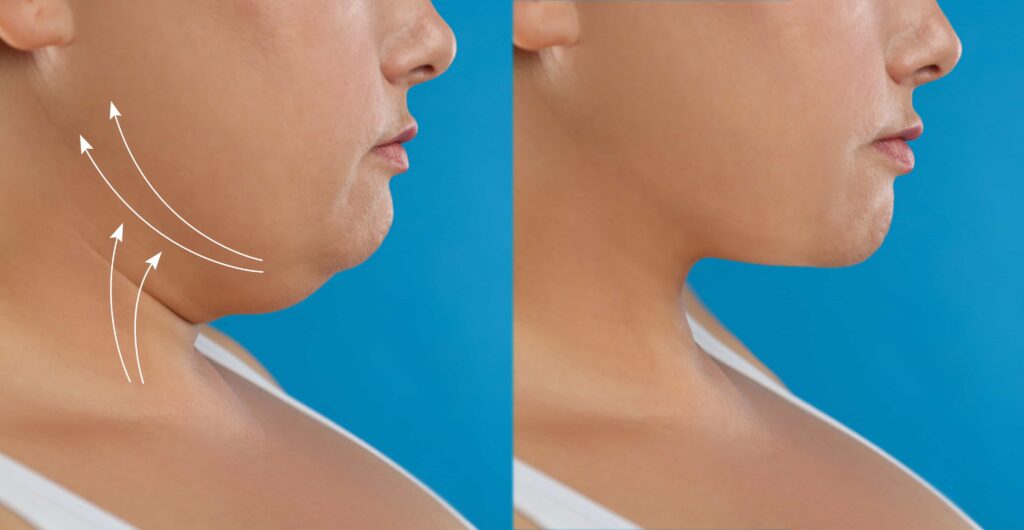
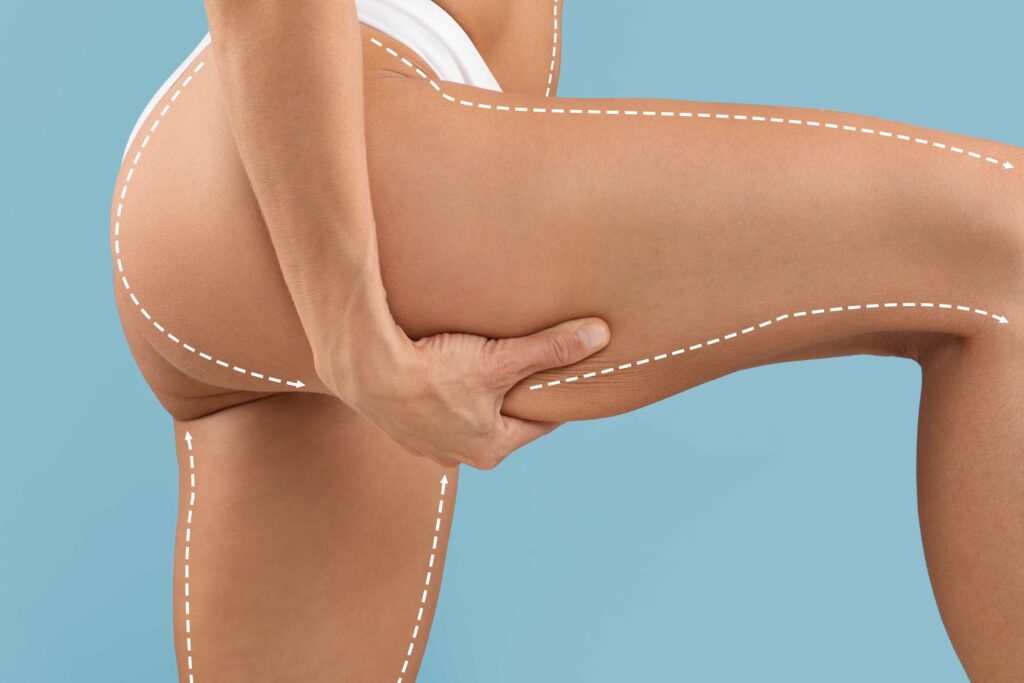
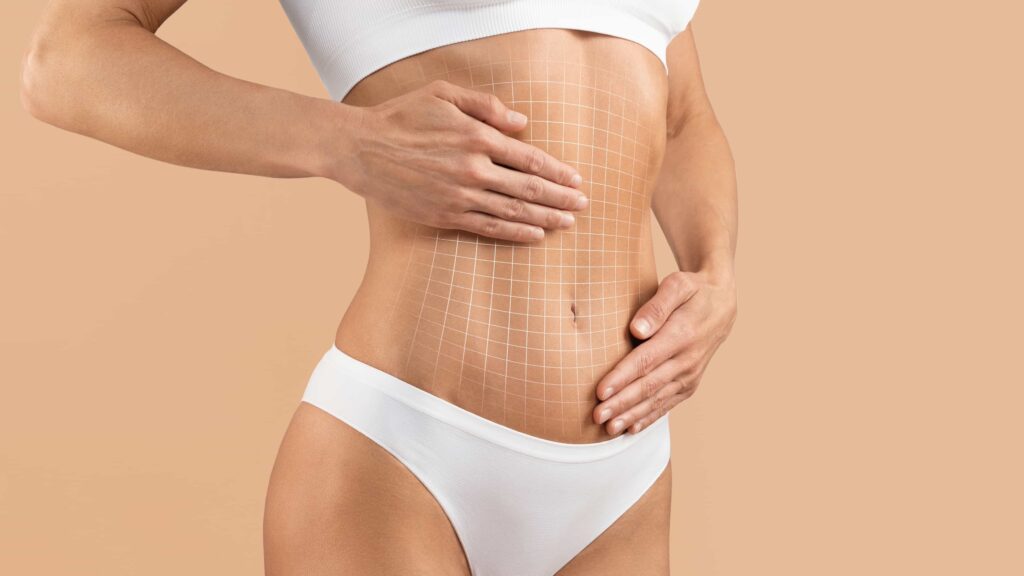
Fat grafting is a procedure that enhances and naturally adds volume to areas of the body by using your own fat.
Fat grafting, also known as autologous fat transfer, is a minimally invasive procedure that improves volume and contour by relocating adipose tissue from one area of body to another.
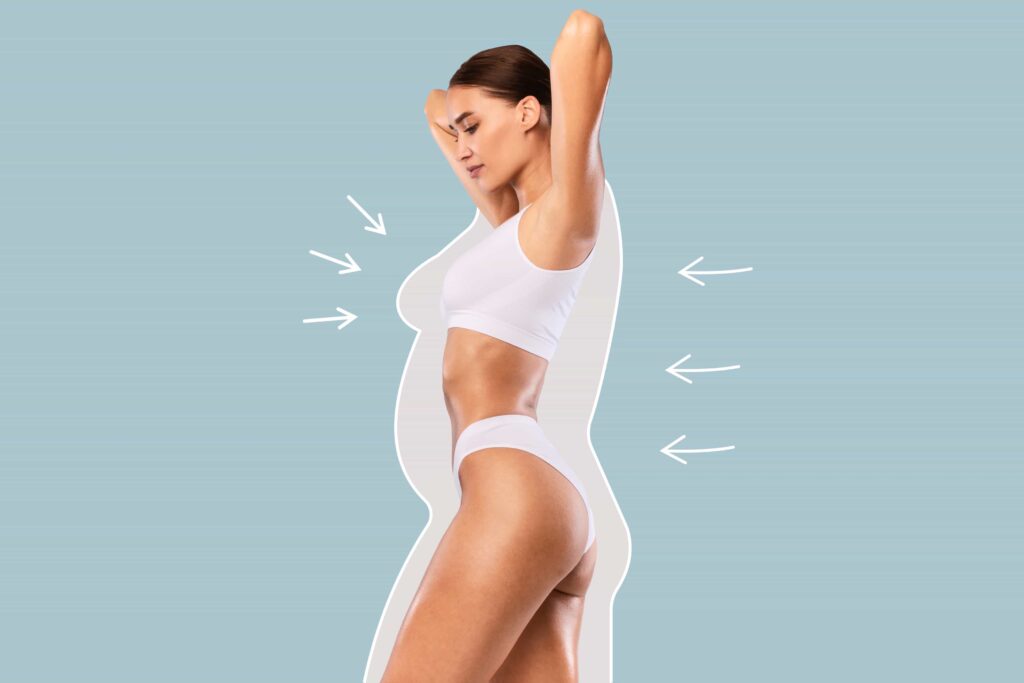

Fat grafting, also called fat transfer, is a simple, low-risk procedure. It involves taking fat from one part of the body and moving it to another area to improve shape or volume. Doctors often use it for cosmetic reasons, but it can also help with reconstruction.
The results of fat transfer can last for many years—and sometimes even decades. Fat grafting is both effective and versatile, making it a popular option for many medical and cosmetic treatments.
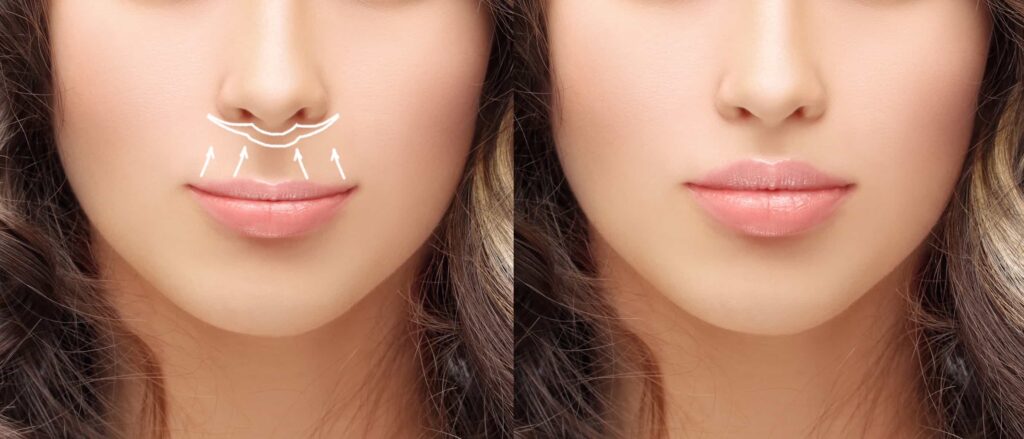
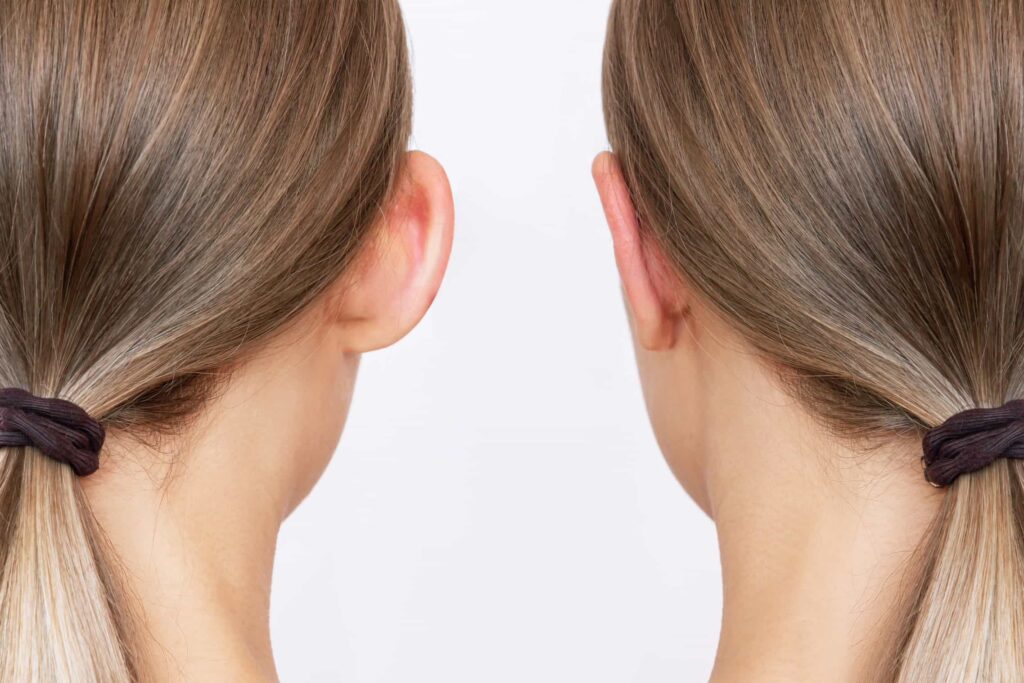
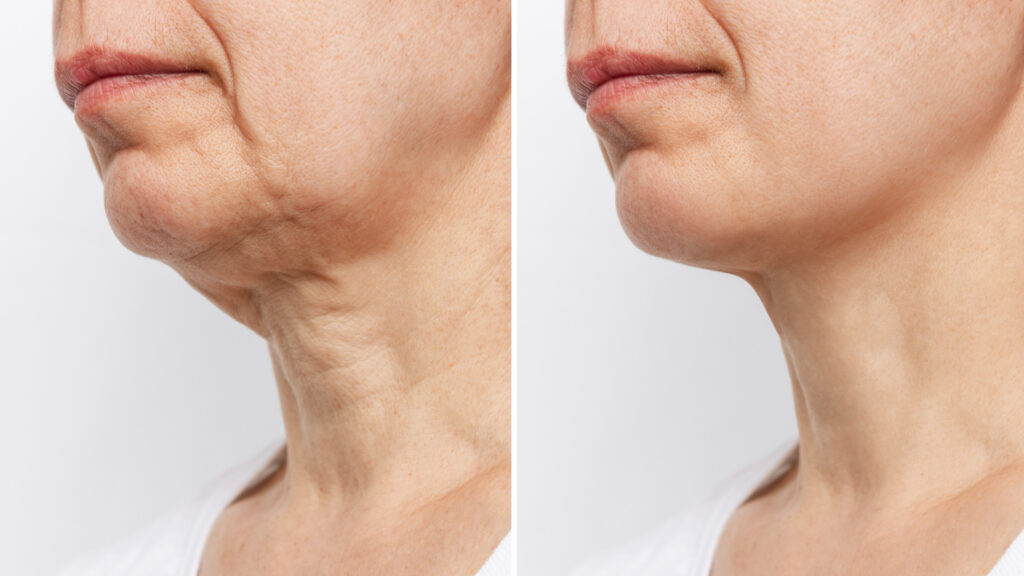
Fat grafting offers many benefits, especially for improving signs of aging and body shape. This technique helps reduce wrinkles and adds volume where it’s needed.
By moving fat from one area to another, it creates a more balanced and natural look. It also restores volume in areas that have become thinner over time. Overall, fat grafting is a flexible way to enhance your body’s appearance.
-Durability of Outcomes: The effects of fat transfer are characterized by a prolonged duration.
-Natural Composition: The fat transfer procedure employs a natural way to volumize the face.
– Minimally Invasive Technique: This approach is less invasive in comparison to traditional surgical facelift procedures.
– Stem Cell Advantages: Adipose tissue contains stem cells, which may facilitate facial rejuvenation.
-Aesthetic Enhancement of Donor Site: The area from which fat is harvested may present a more slender appearance.
-More technically demanding: Fat transfer requires a skilled injection technique compared to dermal fillers.
-Fat absorption: Some transferred fat may be absorbed, resulting in less noticeable effects.
-Longer recovery: Bruising and swelling can last 7–10 days, with final results taking 6–9 months.
-Higher cost: Fat transfer tends to be pricier than injectables, especially for larger volumes.
-Lumps: Improper placement can lead to lumps.
-Risks: Injecting into a vessel can cause tissue damage or visual impairment.
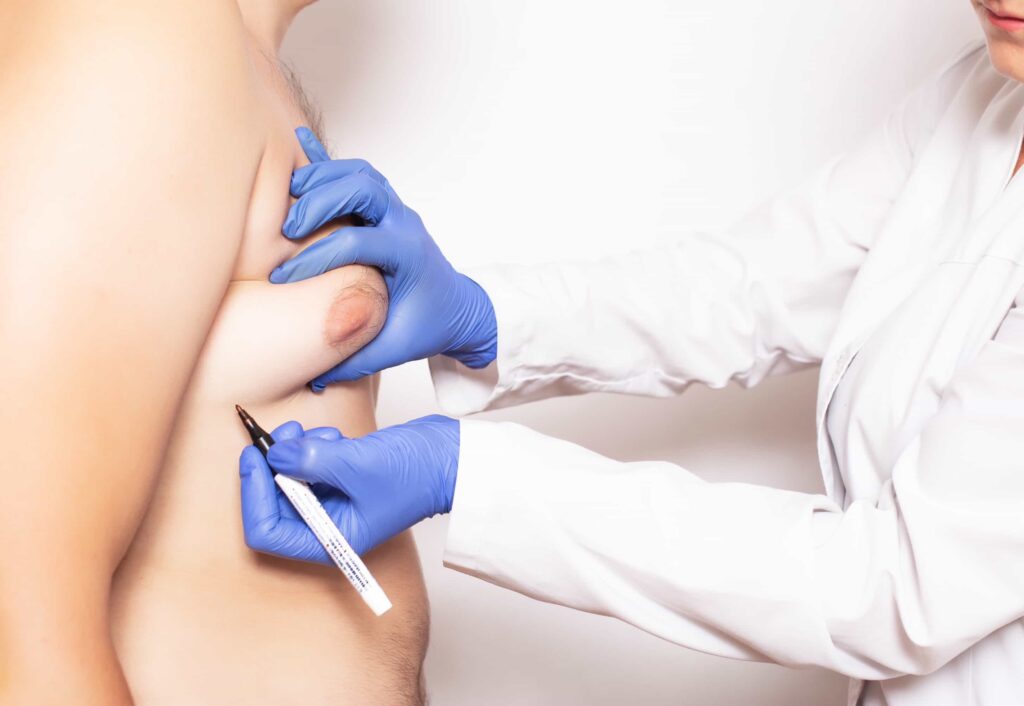
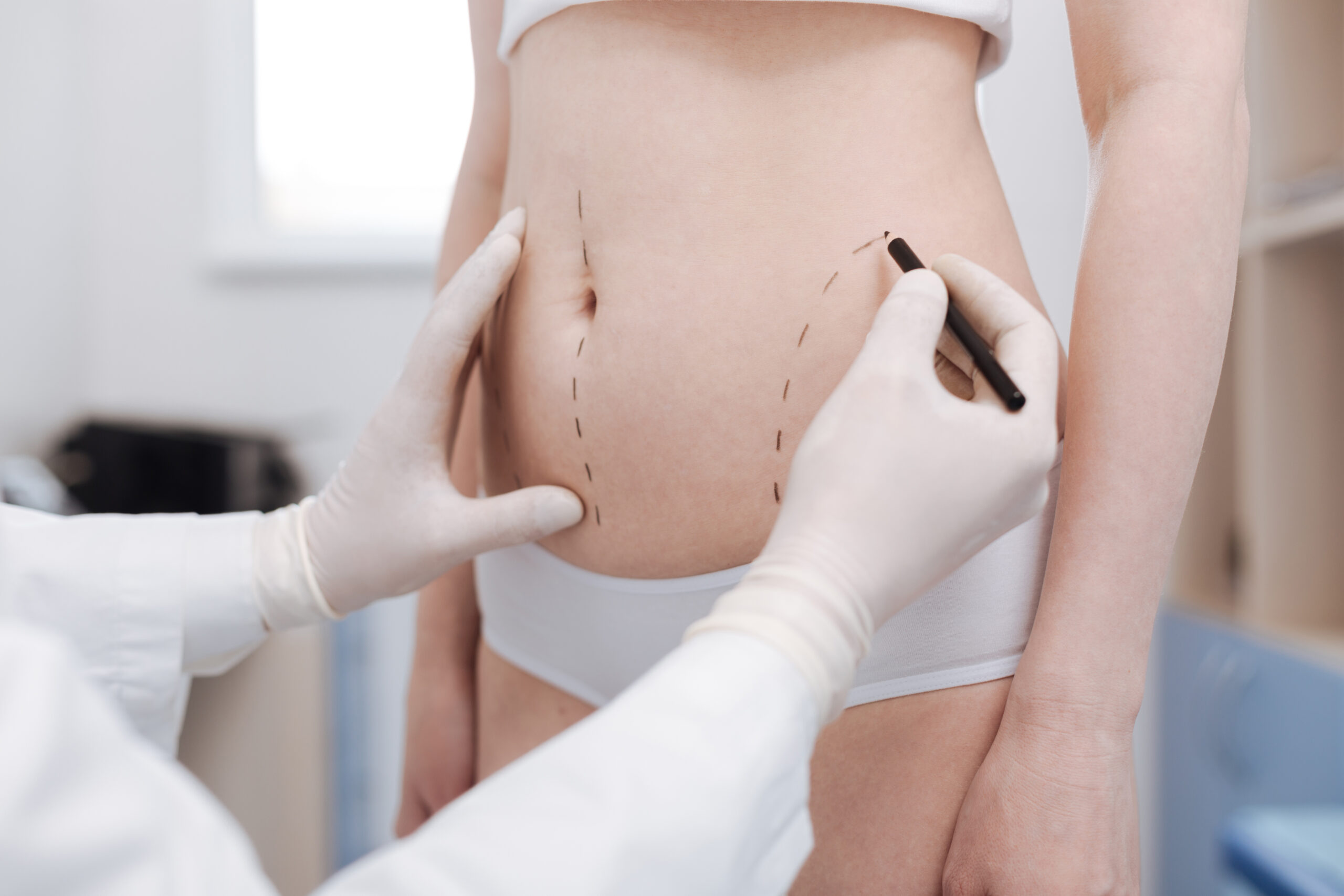
During the procedure, the surgeon usually uses general anesthesia. For smaller areas, local anesthesia may be enough. The surgeon removes fat from areas like the abdomen, flanks, or thighs using liposuction.
After collecting the fat, the surgeon carefully injects it into the target area. The method used depends on the surgeon’s experience and the patient’s needs.
The transferred fat blends with nearby tissue, creating a natural and long-lasting result.
Following the procedure, it is anticipated that bruising and swelling will occur at both the donor and graft sites. The bruising and swelling in the facial area are expected to diminish within one to two weeks; however, the recovery period for the donor sites may extend up to six months.
A fat transfer can yield results that may last for years, decades, or potentially even longer.
Fat grafting is generally safe with few complications, but risks exist. Choose an experienced plastic surgeon skilled in fat transfer. Minor issues like oil cysts and infections can occur but are typically manageable; serious complications are rare.
Expect about 50-60% volume loss, possibly requiring a touch-up, along with common side effects like bruising, swelling, and altered sensation.
The cost of a fat grafting procedure may range from $2,500 to $10,000. The final expense associated with fat grafting is influenced by various factors, including the geographical location, the qualifications of the board-certified facial plastic surgeon, as well as the duration and complexity of the surgical procedure.