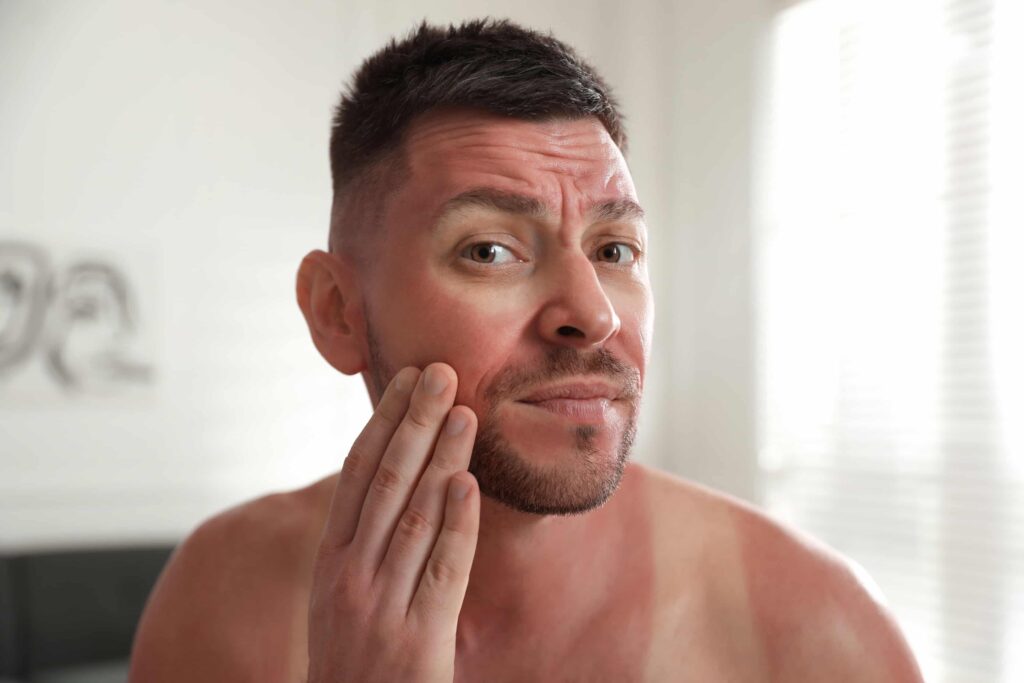
Sun damage refers to the harmful effects that prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can have on the skin. It can manifest as a range of conditions, including sunburn, premature aging, pigmentation disorders, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
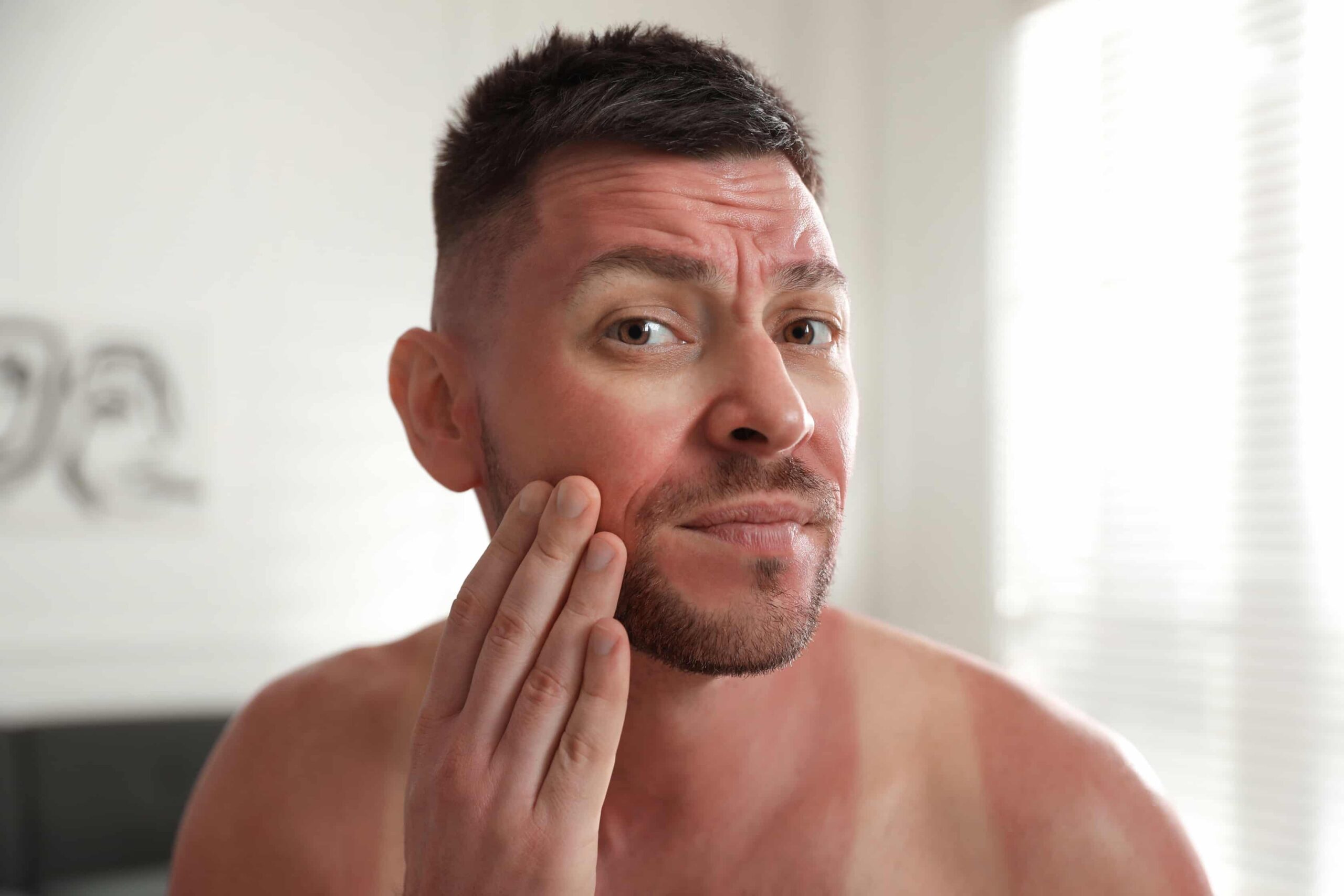
The primary cause of sun damage is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, including both UVA and UVB rays. Factors such as time spent in the sun, geographical location, altitude, and season can impact the degree of sun damage. Failure to use protective measures like sunscreen, hats, sunglasses, and seeking shade can increase the risk of sun damage
Actinic Keratosis is a precancerous condition characterized by rough, scaly patches on the skin caused by long-term sun exposure.
Refers to the cumulative effects of sun exposure over time, leading to premature aging of the skin. Symptoms include fine lines, wrinkles, dryness, rough texture, and uneven pigmentation.
Occurs when the skin becomes red, inflamed, and painful due to overexposure to UV radiation. It is a visible sign of skin damage and can range from mild to severe.
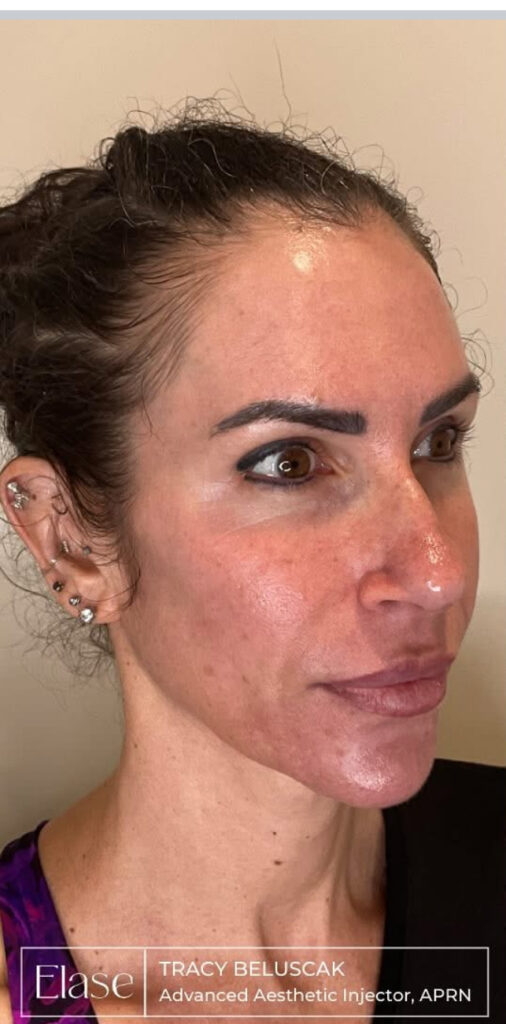
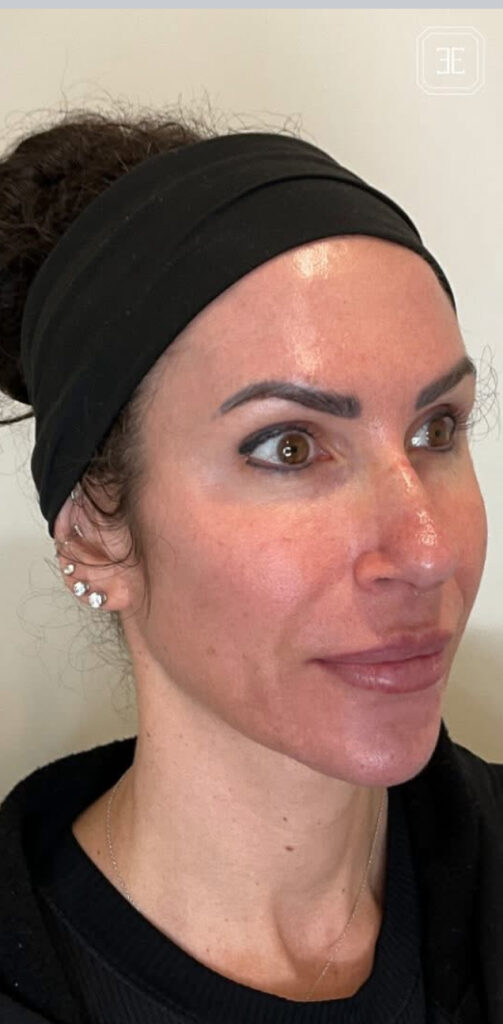
The best way to prevent sun damage is through effective sun protection measures, including wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and using sunglasses.
Moisturizers, retinoids and skin lightening agents. Skincare products containing ingredients like retinol, peptides, exosomes and Vitamin C can stimulate collagen synthesis and help repair sun damage. Moisturizers improves skin hydration and lightening agents can aid in lightening sun spots.