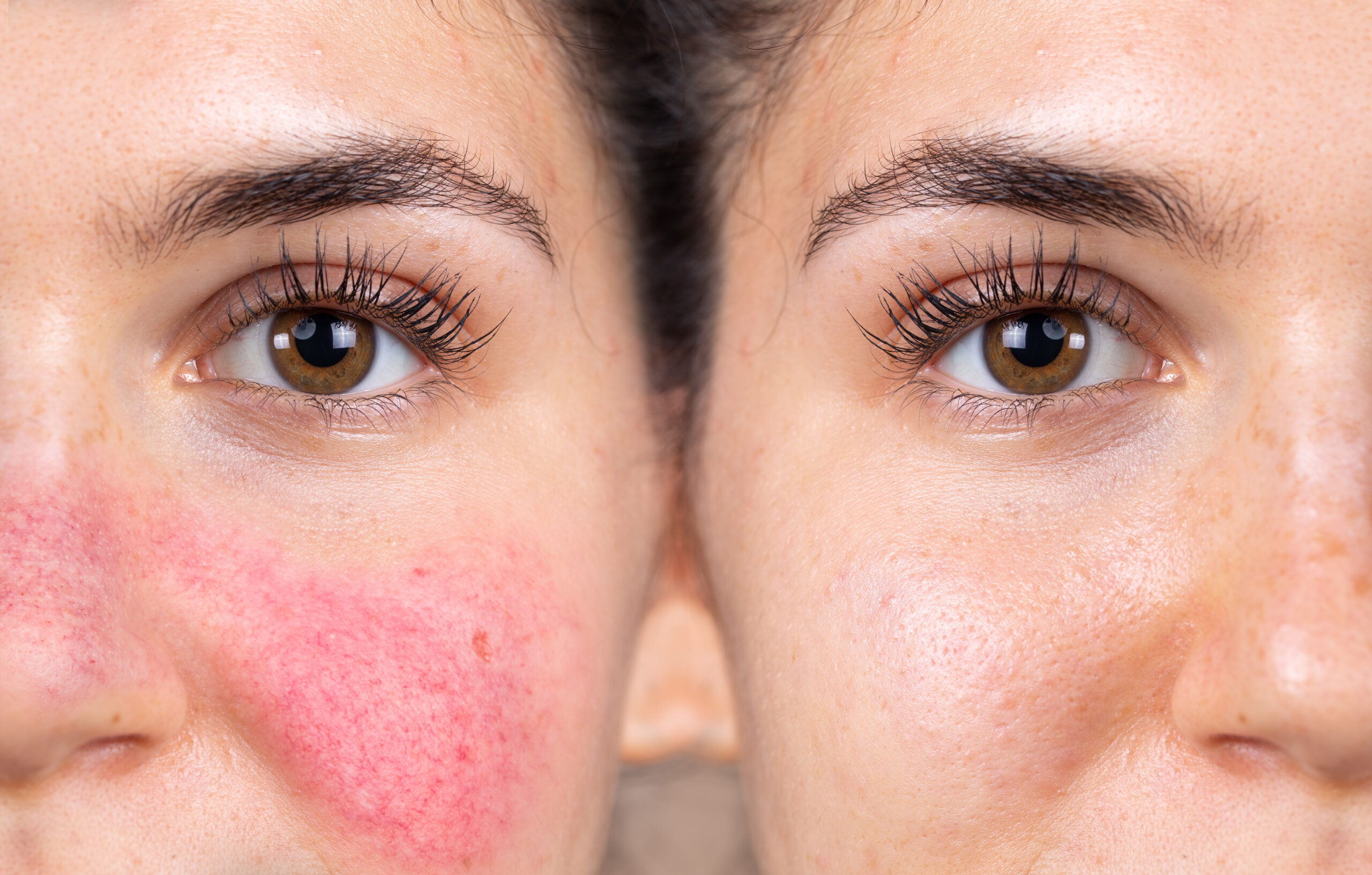
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. Characteristics include redness, flushing, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small, pus-filled bumps.
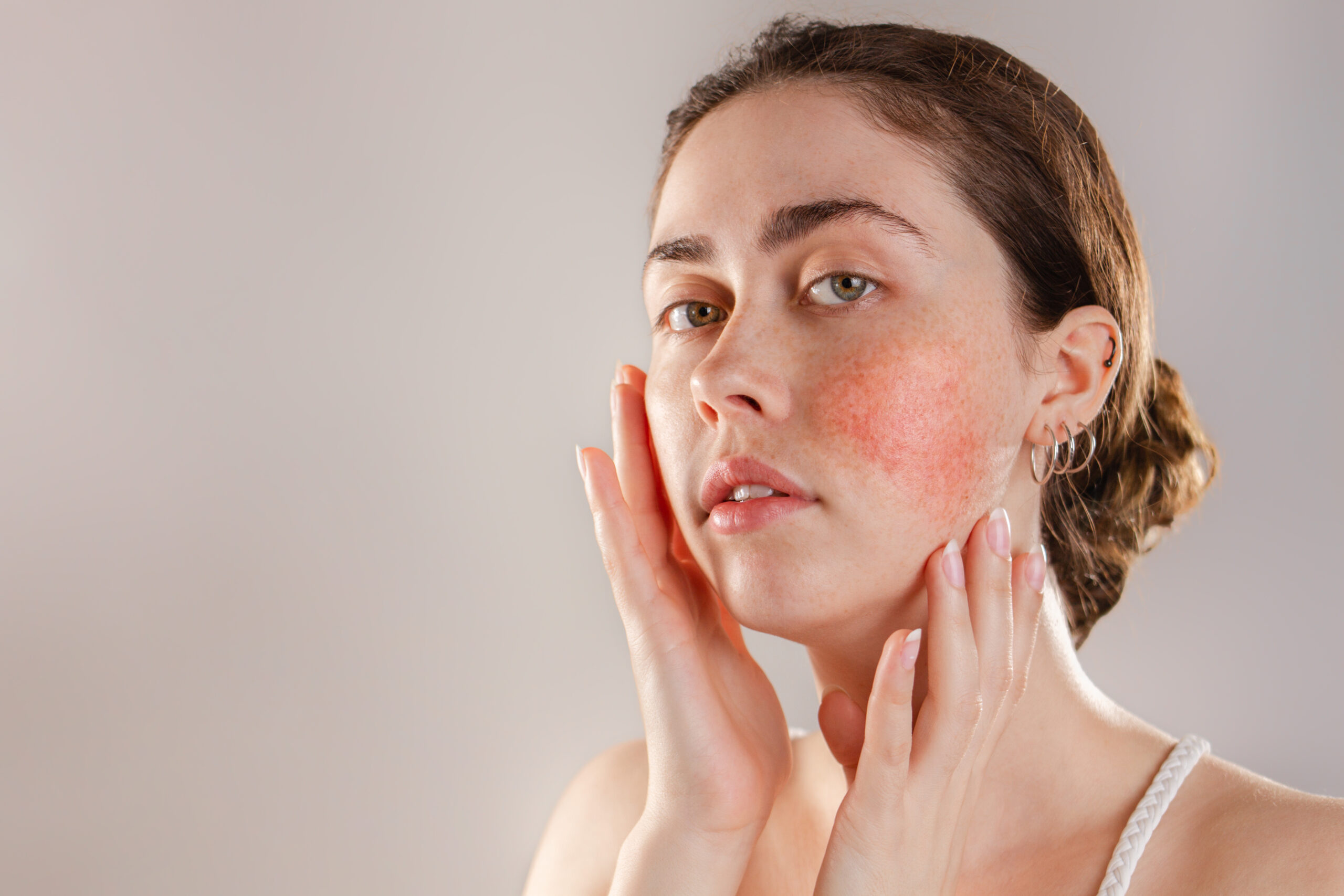

Medical professionals don’t know the exact cause of rosacea but believe several factors contribute to its development.
Rosacea is associated with abnormalities in the face’s blood vessels, causing them to dilate and become more visible. This vascular dysfunction contributes to the persistent redness and flushing seen in rosacea.
A family history of rosacea increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Genetic predisposition may make specific individuals more susceptible to environmental triggers.
Research suggests that an overactive immune system response may play a role in the development of rosacea. Inflammation triggered by the immune system can lead to the characteristic symptoms of the condition.
Various environmental factors can exacerbate rosacea symptoms, including exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, wind, certain foods, alcohol, caffeine, and stress.
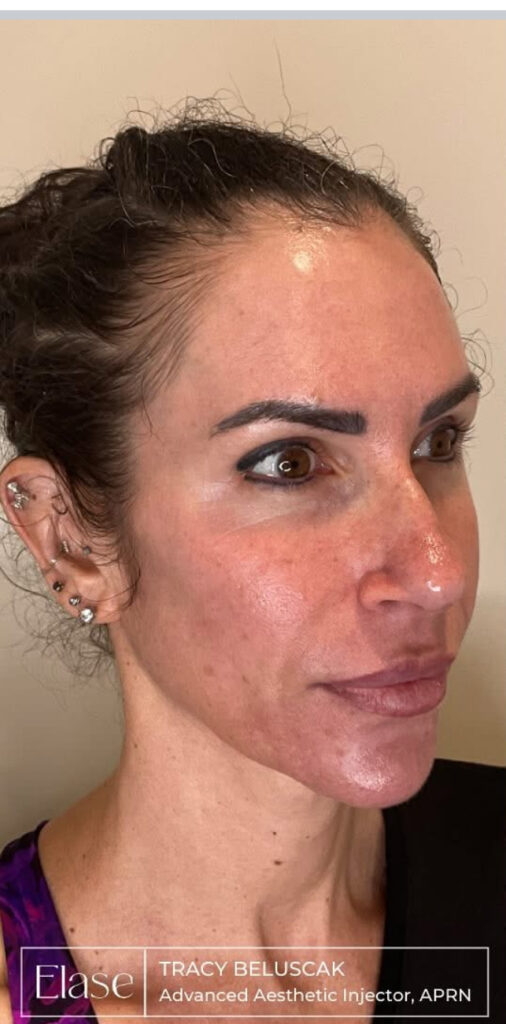
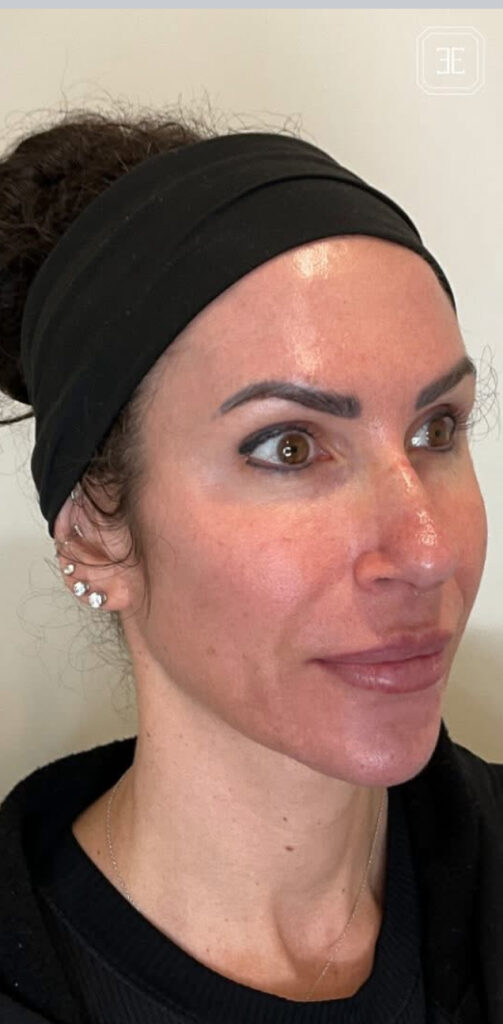
Research indicates that chemical peels, specifically with supramolecular salicylic acid at proper concentrations, can help alleviate symptoms of rosacea.
Gentle skincare routines using mild, non-irritating cleansers and moisturizers are essential for managing rosacea. Avoiding triggers like sun exposure, extreme temperatures, spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can help minimize flare-ups.
Prescription creams and gels containing ingredients like azelaic acid, metronidazole, or sulfur can help reduce redness and inflammation. These medications work by constricting blood vessels, reducing flushing, and improving the skin’s overall appearance.
In more severe cases, a medical provider will prescribe oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or isotretinoin to control inflammation and reduce symptoms. Due to potential side effects, oral medications are typically used for a limited time